Some of the highlights from AWS Re:Invent
- December 2, 2020
- Steve Rogerson
At this week’s AWS Re:Invent, Amazon Web Services, (AWS) made a number of announcements including DevOps Guru, a fully-managed operations service that uses machine learning to make it easier for developers to improve application availability by automatically detecting operational issues and recommending actions for remediation.
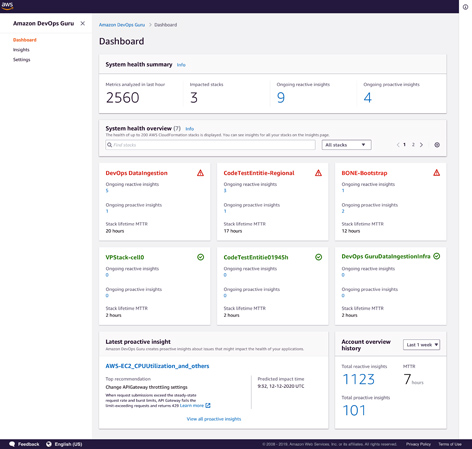
DevOps Guru applies machine learning to collect and analyse automatically data such as application metrics, logs, events and traces for identifying behaviour that deviates from normal operating patterns, for example under-provisioned compute capacity, database IO over-use and memory leak.
When DevOps Guru identifies anomalous application behaviour – increased latency, error rates, resource constraints and so on – that could cause potential outages or service disruptions, it alerts developers with issue details such as resources involved, issue timeline and related events via Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) and partner integrations such as Atlassian Opsgenie and PagerDuty to help them quickly understand the potential impact and likely causes of the issue with specific recommendations for remediation.
Developers can use remediation suggestions from DevOps Guru to reduce time to resolution when issues arise and improve application availability and reliability with no manual setup or machine-learning expertise required. There are no upfront costs or commitments with DevOps Guru, and users pay only for the data DevOps Guru analyses.
AWS also announced four container innovations to help users develop, deploy and scale modern applications. Containers provide a standard way for developers to package and run applications quickly and reliably in any environment, while also improving resource utilisation and reducing cost.
AWS is making it easier to provision, deploy and manage container applications. It is doing this by enabling customers to run Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) or Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) in their own data centres, adding a service for automated container and serverless application development and deployment, and providing a container registry that gives developers an easy and available way to share and deploy container software publicly.
AWS announced three analytics capabilities that improve the performance of Amazon Redshift data warehouses, make it easier to move and combine data across data stores, and make it simpler for end-users to get more value from their business data using machine learning:
- Aqua for Amazon Redshift accelerates querying with a hardware-accelerated cache that brings the compute to the storage and delivers up to ten times better query performance than other cloud data warehouses, with general availability coming in January 2021.
- AWS Glue Elastic Views help developers build applications that use data from multiple data stores with materialised views that automatically combine and replicate data across storage, data warehouses and databases.
- Amazon QuickSight Q delivers a machine-learning-powered capability for QuickSight that gives users the ability to use natural language expressions to ask business questions in the QuickSight Q search bar and receive accurate answers in seconds.
The company also announced the next version of Aurora Serverless, as well as a capability that makes it easier for users to migrate from SQL Server to Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL, and an open source project that helps more organisations migrate off legacy databases to open source alternatives.
For those that don’t want to deal with the work associated with self-managing database capacity, Aurora Serverless v2 scales to hundreds of thousands of transactions in a fraction of a second, delivering up to 90% cost savings compared with provisioning for peak capacity.
Babelfish for Aurora PostgreSQL is a capability for Amazon Aurora that allows users to run SQL Server applications directly on Aurora PostgreSQL with little to no code changes. AWS also shared its plans to open source Babelfish for PostgreSQL under the permissive Apache 2.0 licence and make it available on GitHub.
AWS announced four storage innovations that deliver added storage performance, resiliency and value:
- Amazon EBS io2 Block Express volumes: Storage server architecture delivers a SAN built for the cloud, with up to 256,000 IOPS, 4000Mbyte/s throughput, and 64Tbyte capacity to meet the performance requirements of the IO intensive business critical applications; available in preview.
- Amazon EBS Gp3 volumes: General-purpose SSD volumes for Amazon EBS provide the flexibility to provision additional IOPS and throughput without adding storage, while also offering higher baseline performance of 3000 IOPS and 125Mbyte/s of throughput with the ability to provision up to 16,000 IOPS and 1000Mbyte/s peak throughput at a 20% lower price per Gbyte of storage than existing Gp2 volumes; available today.
- Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering automatic data archiving: Two new tiers – Archive Access and Deep Archive Access – help reduce storage costs by up to 95% for objects rarely accessed by automatically moving unused objects into archive access tiers; available today.
- Amazon S3 Replication (multi-destination): Capability provides the ability to replicate data to multiple S3 buckets in the same or different AWS regions, to manage content distribution, compliance and data-sharing needs across regions; available today.
AWS announced five capabilities for its rapidly growing contact centre service, Amazon Connect, that improve contact centre agent productivity and end-user experiences. Amazon Connect is easy to use, quick to deploy and scalable to up to tens of thousands of agents to help companies of any size improve customer service at a lower cost.
The added capabilities give agents the right information at the right time, provide more personalised service, help managers impact customer interactions during calls, make it faster to authenticate customers more securely, and make customer follow-up tasks easier to manage. These capabilities are powered by AWS’s machine-learning technology, require no technical expertise to use and are available as features within Amazon Connect.
AWS also added five Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, two AWS Outposts form factors, and three AWS local zones locations.
AWS says it already has more compute instance types than any other cloud provider, with instances based on the fastest processors from Intel, cost-optimised instances with AMD processors, GPU instances from Nvidia, instances that feature up to 400Gbit/s networking performance, and the only Arm-based instances in the cloud offering 40% better price performance with AWS-designed Graviton2 processors.
AWS Outposts enable users who want to run AWS on-premises to do so with the same APIs, tools and hardware that they use to run AWS in AWS’s regions. Local zones gives users who need low latency infrastructure in major metropolitan areas but don’t want to provision or maintain data centre space in those locales the ability to use AWS in these metropolitan areas.




